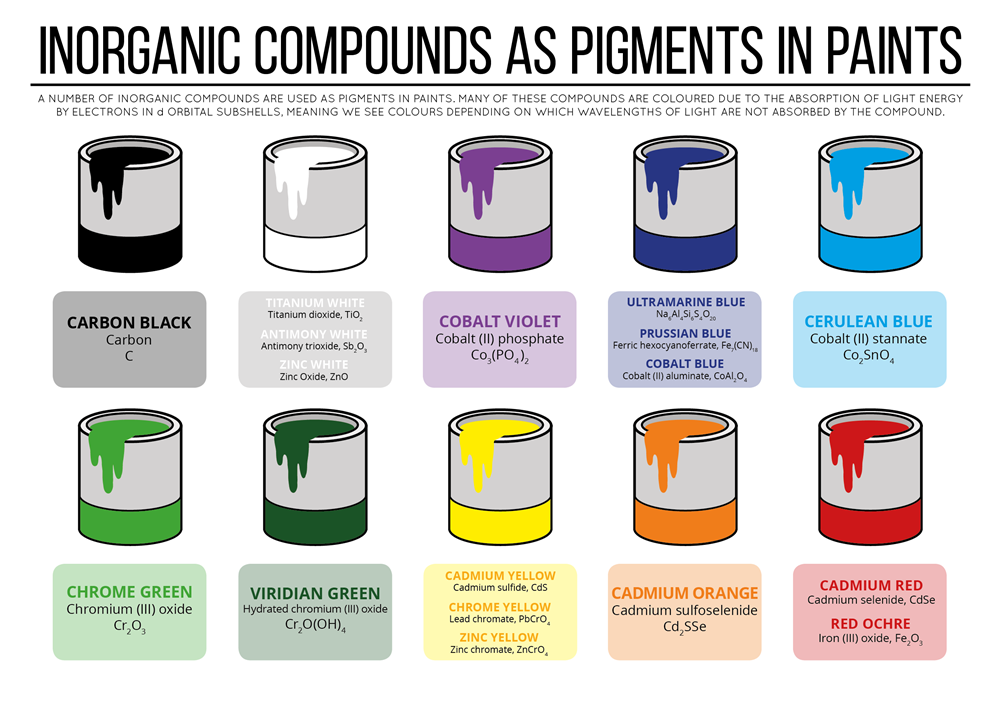
Inorganic pigments play a vital role in various industries, including paints, coatings, plastics, ceramics, and construction materials. These pigments are synthesized from inorganic compounds and minerals, offering a wide range of colors and properties. Understanding their classification and characteristics is crucial for selecting the right pigment for specific applications. Here’s an in-depth exploration:
Classification of Inorganic Pigments:
1.Metallic Pigments:
Aluminum: Aluminum pigments provide metallic effects like silver, gold, and bronze. They are commonly used in automotive coatings, printing inks, and cosmetics.
Iron Oxides: These pigments include red, yellow, and black iron oxides. They offer excellent color stability, opacity, and weather resistance, making them suitable for paints, plastics, and construction materials.
Copper Phthalocyanine: Known for their vibrant blue and green hues, copper phthalocyanine pigments are used in coatings, plastics, and textiles.
Pearlescent Pigments: These pigments create shimmering effects resembling pearls. They consist of mica coated with metal oxides like titanium dioxide or iron oxide. Pearlescent pigments find applications in cosmetics, plastics, and automotive coatings.
2. Non-Metallic Inorganic Pigments:
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2): TiO2 is one of the most widely used white pigments due to its high opacity, brightness, and UV resistance. It’s prevalent in paints, coatings, plastics, and paper.
Carbon Black: Carbon black pigments offer deep black hues and excellent UV resistance. They are extensively used in rubber products, inks, and coatings.
Ultramarine Blue: Derived from the mineral lapis lazuli, ultramarine blue pigments provide intense blue shades and good lightfastness. They are employed in plastics, coatings, and artist’s paints.
Chromium Oxide Green: Known for its durability and resistance to heat and chemicals, chromium oxide green is used in paints, plastics, and ceramics for green coloration.
Characteristics of inorganic pigments:
● Larger particle size
● Usually more opaque, with a better ability to hide the substrate or base color
Low chroma or brightness
● Usually more stable, such as to light or chemicals
● Usually derived from mineral or metal compounds
Advantages and Disadvantages of inorganic pigments:
Inorganic pigments are often a popular choice in industry for a number of reasons, but they also have their drawbacks. Below we list some important positive and negative characteristics of inorganic pigments:
1. Excellent fade resistance: One advantage of inorganic pigments is that they can better withstand the effects of sunlight, climate and chemicals, have excellent fade resistance in light, and they tend to be more resistant to fade when exposed to the open air and high temperatures.
2. Cost Effective: Inorganic pigments tend to be less expensive to produce, especially for the large amounts of pigments required for industrial applications, due in large part to the relatively simple chemical reactions required to produce them.
3. Poor hue: While inorganic pigments tend to hold color well, the color they produce on their own is usually dull, and it is usually only when inorganic pigments are mixed with organic pigments or dyes that the hue and brightness can be improved.
4. Toxicity: Inorganic pigments are more harmful to the environment due to the presence of lead salts in their components. Some are even downright toxic, like lead-based pigments.
That’s all about inorganic pigments,Inorganic pigments encompass a diverse range of materials with unique properties and applications. Understanding their classification and characteristics is essential for selecting the right pigment to achieve desired coloration, performance, and durability in various products and industries.Xuantai Pigment specializes in the production of iron oxide pigments, titanium white, carbon black, welcome customers all over the world to come to consult.
Post time: Apr-23-2024