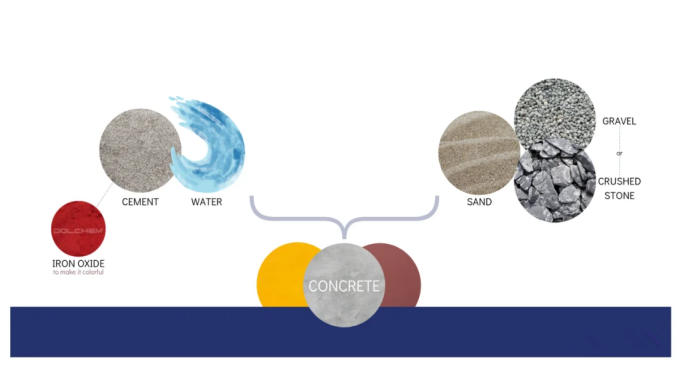
Iron oxide pigments (natural or synthetic iron oxides) are gaining in popularity in industries such as construction, paints and coatings, plastics, and textiles. Sought after for their ability to provide color and durability to products, they are both cost-effective and eco-friendly relative to other colorants.
Nevertheless, as they carry significant environmental and energy impacts, the effects of the production of iron oxide pigments cannot be overlooked. There are several advantages and disadvantages to utilizing iron oxide pigments. The measures being taken to reduce adverse effects on energy consumption and the environment are discussed below.
The Advantages of Iron Oxide Pigments
Iron oxide pigments are derived from natural minerals or synthesized chemically and have several advantages over other colorants, including:
- Durability: Resistant to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical degradation. Fading and discoloration are minimal, making them ideal for outdoor applications.
- Stability: Stable in various pH levels and temperatures, making them suitable for use in different types of products.
- Safety: Non-toxic, non-carcinogenic, and does not pose a health risk to humans or the environment.
- Cost-effectiveness: Readily available, and the cost is lower than organic pigments or dyes.
Challenges and Opportunities in a Changing Landscape
The iron oxide market is expected to experience both challenges and opportunities in the coming years, according to a comprehensive analysis by FMI Blog. Notwithstanding, there is increasing demand for iron oxide in various applications such as: Construction Automotive Electronics industries.
Challenges:
- The volatility of raw material prices as well as stringent regulations regarding environmental and occupational safety.
- The emergence of substitutes for iron oxide (synthetic iron oxide and other pigments) could pose a threat to the market’s growth.
- Companies in the iron oxide market must focus on product innovation, sustainability practices, and expanding their product portfolio.
The Environment and Energy Impacts of Iron Oxide Pigments
Iron oxide extraction involves both the mining and processing of natural minerals or chemical synthesis. This process can have negative impacts on the environment, such as soil erosion, habitat destruction, and loss of biodiversity, due to the extraction of iron oxide minerals. Additionally, mining operations may result in water pollution, especially if the mines are situated near water bodies.
The utilization of chemical solvents and reagents during production processes can contribute to the discharge of deleterious pollutants into the atmosphere and water bodies. Such pollutants can have a profound impact on both human health and wildlife, thereby necessitating the implementation of rigorous regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing any adverse environmental consequences resulting from production activities.
Apart from environmental considerations, an additional key concern is the considerable energy consumption associated with the production of these products, leading to elevated greenhouse gas emissions.
Repurposing of Abandoned Mines is a Net Positive
Mining sites that have been abandoned for decades are now being utilized to produce iron oxide pigments. The innovative use of old mines provides a new source of pigments and helps in the rehabilitation of degraded land. The process involves extracting iron oxide from the waste materials left behind in abandoned mines. The extracted iron oxide is then turned into pigments which reduces the need for new mining activities and also helps to mitigate their environmental impact.
Although iron oxide pigments offer benefits, their production and use can have significant environmental and energy impacts. Various efforts including recycling, sustainable sourcing, clean production, and regulation are helping.
Recycling:
- Recycling from waste or industrial by-products can reduce the demand for virgin pigments and minimize waste disposal.
- Sustainable sourcing: Natural minerals or renewable energy in the production of iron oxide pigments can reduce the environmental impact.
- Clean production: Energy-efficient processes and reduced emissions, can minimize energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Regulation: Important to ensure compliance with environmental and safety standards and minimize their negative effects.
(This article all comes from the Internet)
Post time: Apr-25-2023